- Tétrahydrométhanoptérine
-
Tétrahydrométhanoptérine 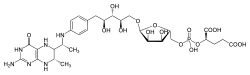
Structure de la tétrahydrométhanoptérineGénéral No CAS PubChem ChEBI SMILES InChI Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C30H45N6O16P [Isomères] Masse molaire[1] 776,6827 ± 0,0332 g·mol-1
C 46,39 %, H 5,84 %, N 10,82 %, O 32,96 %, P 3,99 %,Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. La tétrahydrométhanoptérine, abrégée en THMPT ou H4MPT, est une coenzyme intervenant dans la méthanogenèse chez les archées méthanogènes. C'est un activateur de groupe C1 réduit au niveau méthyle –CH3 avant transfert à la coenzyme M[2]. La tétrahydrosarcinaptérine, abrégée en THSPT ou H4SPT, est une forme modifiée de la THMPT dans laquelle un groupe glutamyle est lié au groupement terminal 2-hydroxyglutarique.
Rôle dans la méthanogenèse
Le N-formylméthanofurane transfère son groupe C1 au site N5 de la ptérine pour donner la formyl-THMPT[3]. Le groupe formyle se condense alors au sein de la molécule pour donner la méthényl-THMPT+, réduite ensuite en méthylène-THMPT[4] par une méthylènetétrahydrométhanoptérine déshydrogénase (EC ).
La méthylène-THMPT est ensuite convertie en méthyl-THMPT par une méthylènetétrahydrométhanoptérine réductase (EC ) avec la coenzyme F420 comme source d'électrons.
La méthyl-THMPT transfère enfin son méthyle à la coenzyme M sous l'action de la tétrahydrométhanoptérine S-méthyltransférase[2] (EC ).
Comparaison avec l'acide tétrahydrofolique
La tétrahydrométhanoptérine est à rapprocher de l'acide tétrahydrofolique, abrégé en THFA ou H4FA dans la littérature anglophone, la principale différence étant la présence sur cette dernière molécule d'un groupe carbonyle C=O sur le cycle benzénique qui en facilite la réduction par rapport à la THMPT. Cette réduction est réalisée par une protéine fer-soufre[4].
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) R. K. Thauer, « Biochemistry of Methanogenesis: a tribute to Marjory Stephenson », dans Microbiology, 1998, 144, 2377-2406.
- (en) P. Acharya, E. Warkentin, U. Ermler, R. K. Thauer, S. Shima, « The Structure of Formylmethanofuran:Tetrahydromethanopterin Formyltransferase in Complex with its Coenzymes », dans Journal of Molecular Biology, 2006, 357, 870-879.
- (en) M. Korbas, S. Vogt, W. Meyer-Klaucke, E. Bill, E. J. Lyon, R. K. Thauer, et S. Shima, « The Iron-Sulfur Cluster-free Hydrogenase (Hmd) Is a Metalloenzyme with a Novel Iron Binding Motif », dans Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2006, 281, 30804-30813.
Catégories :- Composé du phosphore
- Coenzyme
- Méthanogenèse
- Ptérine
- Aminobenzène
- Organophosphate
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
