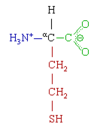
- Homocysteine
-
Homocystéine
Homocystéine Formule développée de l'homocystéine Général Nom IUPAC acide (S)-2-amino-4-sulfanyl-butanoïque No CAS (DL) No EINECS (DL) PubChem Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C4H9NO2S [Isomères]
HSCH2CH2CH(NH2)CO2HMasse molaire 135,185 g∙mol-1
C 35,54 %, H 6,71 %, N 10,36 %, O 23,67 %, S 23,72 %,Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. L'homocystéine est un acide aminé soufré résultant du catabolisme de la méthionine ou de la cystathionine. Son nom provient de sa structure analogue avec la cystéine, cet autre acide aminé ayant un groupement méthylène (-CH2-) en moins. Son augmentation résulte le plus souvent d'une carence en cobalamine (vitamine B12) ou en acide folique (vitamine B9).
L'hyperhomocystéinémie est un excés d'homocystéine dans le plasma sanguin.
- 9 µmol/L = Hyperhomocystéinémie légère modéré
- 11-25 µmol/L = Hyperhomocystéinémie légère modéré
- 25-50 µmol/L = Hyperhomocystéinémie intermédiaire
- 50-500 µmol/L = Hyperhomocystéinémie sévère
Il s'agit d'une substance pro-inflammatoire dont le rôle dans l'athérosclérose a été suspecté en 1969 par McCully et qui est largement prouvé de nos jours. Il n'est pas encore prouvé si la relation entre des niveaux élevés d'homocystéine dans le serum est causale pour l'athérosclérose ou si une homocystéinémie élevée n'est qu'un indicateur. L'homocysteine a été également incriminée dans le mécanisme de certaines affections neuropsychiatriques. Ainsi, elle serait un facteur de risque pour la maladie d'Alzheimer[réf. nécessaire], le défaut de fermeture du tube neural[1], les troubles dépressifs[2] ainsi que pour la schizophrénie[3]. Son taux semble également être corrélé avec le risque de survenue d'une dégénérescence maculaire liée à l'âge[4]..
La supplémentation artificielle en acide folique et en vitamine B6 et B12, chez des patients à hauts risques de maladie coronarienne, baisse de manière significative le taux d'homocystéine mais ne diminue en aucun façon la fréquence d'une atteinte cardio-vasculaire [5],[6]
Quelques formes congénitales d'hyperhomocystéinémie ou -urie sont décrites. Il existe, dans ces cas, une majoration du risque de faire un accident cardio-vasculaire et la supplémentation en vitamines semble avoir montré, dans ces cas, un intérêt.
Voir aussi
Articles connexes
Références
- ↑ Zammit S, Lewis S, Gunnell D, Smith GD, Schizophrenia and neural tube defects: comparisons from an epidemiological perspective, Schizophr Bull. 2007 Jul;33(4):853-8
- ↑ Folstein M, Liu T, Peter I, Buell J, Arsenault L, Scott T, Qiu WW, The homocysteine hypothesis of depression, Am J Psychiatry. 2007 Jun;164(6):861-7. Review. Erratum in: Am J Psychiatry. 2007 Jul;164(7):1123.
- ↑ Muntjewerff JW, Kahn RS, Blom HJ, den Heijer M, Homocysteine, methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase and risk of schizophrenia: a meta-analysis, Mol Psychiatry, 2006 Feb;11(2):143-9
- ↑ Heuberger RA, Fisher AI, Jacques PF et als. Relation of blood homocysteine and its nutritional determinants to age-related maculopathy in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, Am J Clin Nutr, 2002;76:897-902
- ↑ (en)The Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) 2 Investigators, Homocysteine lowering with folic acid and B vitamins in vascular disease, New Eng J Med, 2006;354:1567-1577
- ↑ (en)Bønaa K, Njølstad I, Ueland P et als. Homocysteine lowering and cardiovascular events after acute myocardial infarction, New Eng J Med, 2006;354:1578-1588
- Portail de la biochimie
- Portail de la chimie
- Portail de la médecine
Catégorie : Acide aminé
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.