- Grassmann
-
Hermann Günther Grassmann
Hermann Günther Grassmann (15 avril 1809 à Stettin - 26 septembre 1877 à Stettin) était un polymathe allemand. À son époque, il était connu en tant que linguiste et est de nos jours reconnu en tant que mathématicien. Il était aussi physicien, néo-humaniste, érudit et un éditeur.
Sommaire
Biographie
Hermann Grassman était le troisième des douze enfants de Justus Günter Grassman et de Johanne Luise Friederike Medenwald. Son père enseignait les mathématiques et la physique au Gymnasium de Stettin en Pologne. Enfant, il a été éduqué par sa mère. Il entra plus tard au Gymnasium de Stettin où son père enseignait. Il partit à Berlin en 1827 pour aller étudier la théologie à l'université de Berlin. Il prit là bas des cours de théologie, de littérature classique, de philosophie, mais pas de mathématiques ou de physique. Il devint professeur assistant à l'université de Berlin en 1832. C'est vers cette période qu'il fit ses premières recherches importantes en mathématiques. En 1834, Grassman commença d'enseigner les mathématiques à Berlin. Un an plus tard, il retourna à Stettin pour enseigner les mathématiques, la physique, l'allemand, le latin et la théologie. Il passa des examens pour enseigner les mathématiques, la physique, la chimie et la minéralogie. En 1852, il eut un poste semblable à celui de son père au gymnasium de Stettin. En 1847, il demanda un poste universitaire au ministre prussien de l'éducation. Celui-ci demanda à Ernst Kummer un avis sur Grassman. Kummer écrivit alors que Grassman avait écrit des choses intéressantes, mais exprimée sous une forme insuffisante. Cette note priva Grassman de toute chance d'obtenir un poste universitaire.
Durant les agitations politiques en Allemagne en 1848 et 1849, Hermann et son frère Robert Grassmann publièrent un article dans un journal pour appeler à ce que Allemagne devienne une monarchie constitutionnelle.
Grassmann éleva sept enfants dont l'un, Hermann Ernst Grassmann, devint professeur de mathématiques à l'université de Gießen.
L'apport spécifique
Il apporte, "en marge des milieux académiques" (source : Dimathème), une méthode de calcul que l'on peut définir aujourd'hui comme le calcul vectoriel.
En 1844, il publia son oeuvre la plus importante Die Lineare Ausdehnungslehre, ein neuer Zweig der Mathematik [L'enseignement de l'extension linéaire, une nouvelle branche des mathématiques].
Il définit le produit extérieur, qui deviendra, en dimension 3, avec Willard Gibbs et William Kingdon Clifford, le produit vectoriel usuel.
On lui doit le théorème des dimensions, qu'on appelle aussi formule de Grassmann :
E étant un espace vectoriel de dimension finie, si F1 et F2 sont deux sous-espaces vectoriels de E, alors
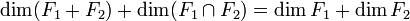 .
.Bibliographie
Primaire :
- 1844. Die lineale Ausdehnungslehre. Leipzig: Wiegand. English translation, 1995, by Lloyd Kannenberg, A new branch of mathematics. Chicago: Open Court. This is A1.
- 1861. Lehrbuch der Mathematik fur hohere Lehrenstalten, Band 1. Berlin: Enslin.
- 1862. Die Ausdehnungslehre, vollstandig und in strenger Form bearbeitet. Berlin: Enslin. English translation, 2000, by Lloyd Kannenberg, Extension Theory. American Mathematical Society. This is A2. Excerpt translated by D. Fearnley-Sander.
- 1894-1911. Gesammelte mathematische und physikalische Werke, in 3 vols. Friedrich Engel ed. Leipzig: B.G. Teubner. Reprinted 1972, New York: Johnson.
Secondaire :
- Hans-Joachim Petsche: Graßmann. Basel [usw.] 2006 (Vita Mathematica 13), ISBN 3-7643-7257-5
Voir aussi
- Algèbre extérieure (aussi connue sous le nom d'algèbre de Grassmann)
- Nombre de Grassmann
- Grassmannien
- Grassmannienne
- Loi de Grassmann
- Commission internationale de l'éclairage (lois de Grassmann sur les couleurs)
Liens externes
H.G. Grassmann [1]
Liens internes
- Portail des mathématiques
Catégories : Naissance en 1809 | Décès en 1877 | Mathématicien allemand
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

