- Buckminsterfullerène
-

« C60 » redirige ici. Pour le paquebot, voir Himalaya (paquebot). Buckminsterfullerène 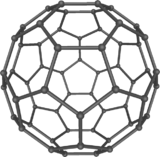
Buckminsterfullerène C60 Général No CAS SMILES InChI Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C60 [Isomères] Masse molaire[3] 720,642 ± 0,048 g·mol-1
C 100 %,Diamètre moléculaire 1,002 nm [1]
(diamètre interne : 0,348 nm [2])Propriétés physiques T° fusion >280 °C[4] Solubilité Insoluble dans l'eau[4] Masse volumique 1,65 g·cm-3 [4] Pression de vapeur saturante 0,01862 mmHg (569,85 °C)[4] Cristallographie Système cristallin cubique Classe cristalline ou groupe d’espace Pa3 [5] Paramètres de maille a = b = c = 14,041 Å
α = β = γ = 90,00 °
Z = 4[5]Volume 2 768,18 Å3 [5] Densité théorique 1,729 [5] Précautions Directive 67/548/EEC[4] 
XiPhrases R : 36/37, Phrases S : 26, 36, NFPA 704[4] SGH[6] 
AttentionUnités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. Le buckminsterfullerène, parfois également appelé footballène est une molécule sphérique en C60 de la famille des fullerènes C2n, structures fermées composées de (2n-20)/2 hexagones et de 12 pentagones. C'est la plus petite du groupe, dont les atomes sont aux sommets d'un icosaèdre tronqué, i.e. forment la même structure qu'un ballon de football. C'est également le fullerène le plus fréquent.
Découvert par Harold Kroto, Robert Curl et Richard Smalley, prix Nobel de chimie en 1996, il est nommé ainsi en l'honneur de Buckminster Fuller, architecte américain, inventeur du dôme géodésique.
Sommaire
Structure
Le buckminsterfullerène a une structure fermée composée de 20 hexagones et 12 pentagones, aux sommets desquels se trouvent les atomes de carbone. Chaque pentagone est entouré de cinq hexagones.
Le groupe de symétrie ponctuelle du C60 est 53m en notation de Hermann-Mauguin (Ih en notation de Schoenflies) : tous les atomes de carbone occupent des sites équivalents.
Les liaisons covalentes doubles 6:6 (entre deux hexagones) sont plus courtes que les liaisons simples 6:5 (entre un hexagone et un pentagone) : 0,140 nm pour les liaisons 6:6 et 0,146 nm pour les liaisons 5:6[7].
Applications
Cette molécule est très utilisée en nanotechnologies, en particulier comme roues dans la fabrication de nanomachines (nanovoitures, nanodragsters, etc.)[8].
Le C60 a aussi la propriété rare et remarquable de former, avec le tétrakis(diméthylamino)éthylène, un aimant purement organique en dessous de 16,1 K[9].
Articles connexes
Notes et références
- (en) H. Tanaka et K. Takeuchi, « Diameter determination of C60 and C70 monomers in the gas phase using a differential mobility analyzer », dans Applied Physics A: Materials Science & Processing, Springer Berlin / Heidelberg, vol. 80, no 4, février 2005, p. 759-761 (ISSN 0947-8396 et 1432-0630) [lien DOI]
- (en) Physical Properties of Fullerenes sur sesres.com. Consulté le 1er janvier 2010
- Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Carbon (fullerene-C60) sur ull.chemistry.uakron.edu. Consulté le 24 octobre 2009
- (en) Fullerene C60 sur www.reciprocalnet.org. Consulté le 12 décembre 2009
- SIGMA-ALDRICH
- (en) K. Hedberg, L. Hedberg, D.S. Bethune, C.A. Brown, H.C. Dorn, R.D. Johnson et M. de Vries, « Bond Lengths in Free Molecules of Buckminsterfullerene, C60, from Gas-Phase Electron Diffraction », dans Science, vol. 254, no 5030, 1991, p. 410-412 [lien DOI]
- (en) Guillaume Vives, JungHo Kang, Kevin F. Kelly et James M. Tour, « Molecular Machinery: Synthesis of a “Nanodragster” », dans Org. Lett., vol. 11, no 24, 2009, p. 5602–5605 [lien DOI]
- (en) Pierre-Marc Allemand, Kishan C. Khemani, Andrew Koch, Fred Wudl, Karoly Holczer, Steven Donovan, George Grüner et Joe D. Thompson, « Organic Molecular Soft Ferromagnetism in a Fullerene C60 », dans Science, vol. 253, no 5017, 1991, p. 301-302 [lien DOI]
- Portail de la chimie
- Portail des micro et nanotechnologies
Catégories :- Produit chimique irritant
- Fullerène
- Forme du carbone
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

